Perception Action Coupling in the Remote Active Telepresence
Background Robots have consistently demonstrated their value as indispensable human assistants, with widespread applications especially in executing remote tasks. One notable example is the tele-nursing robot, which offers essential support and aid in the medical field. However, constructing a dependable tele-robotic system presents numerous challenges, with one of the biggest concerns being how to address the perception issues. Potential challenges could be unconventional viewpoints, limited field of view, and loss of depth. Lack of adequate visual feedback could result in a decrease in the operator's situational awareness, significantly impacting their performance.
Overview With the objective of creating effective interfaces to enhance visual assistance for telerobotics, I developed a physical wearable multi-camera system which includes cameras, headset and trackers. The camera transmits collected RGB views to the headset for presence as the visual feedback. Users can easily switch between different cameras according to their preferences while performing tasks. In additional, the headset is equipped with gaze tracking to capture the user's attention, and the motion trackers can record the user's body movements. By studying how subjects utilize their actions in conjunction with visual input during experiments using this system, we can facilitate the design of a powerful telerobotics platform for human-robot collaboration, and improve some aspects such as the autonomous camera view selection for perception and camera positioning for ergonomic considerations.
Summary
- Design and build a multi-camera physical platform with cameras, headset and motion trackers
- Integrate gaze tracking in HTC VR headset and develop an algorithm for calculating the fixation time
- Utilize Unity as the intermediary for transmitting camera views and voice input for camera switching
- Undertake the design and execution of a user study, carefully observing and analyzing the participants' behavior throughout the experiment
Result
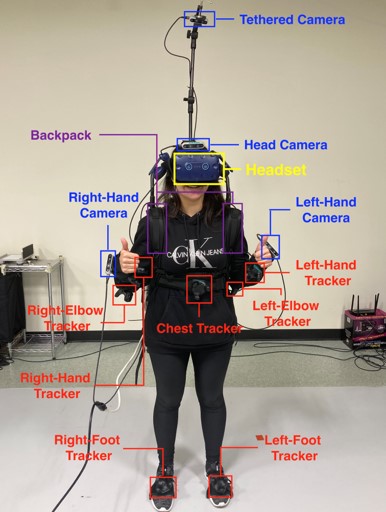
Physical Wearable Multi-Camera System
Experiment
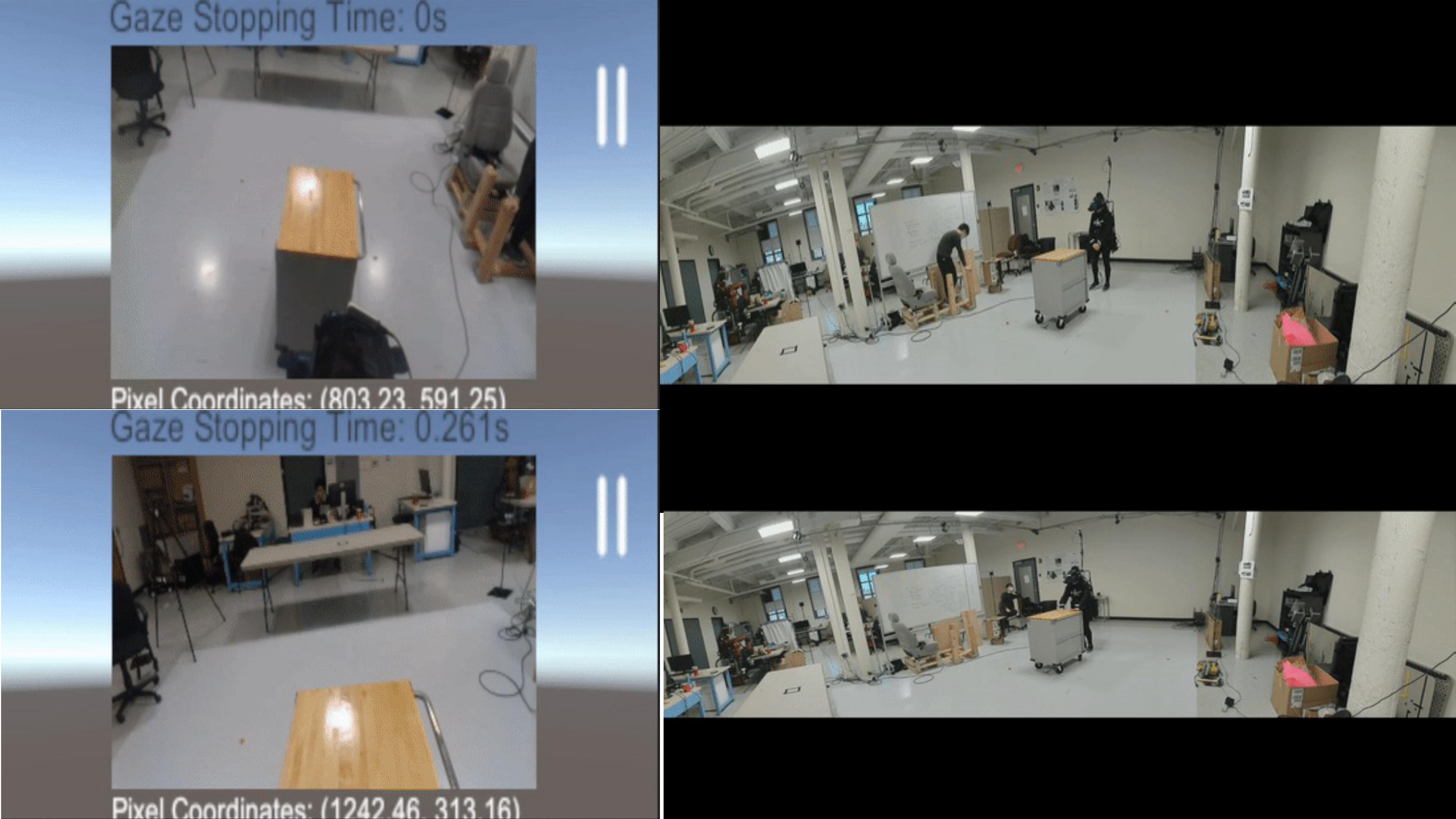

Demo for Navigation Experiment Using Two Cameras (Tethered vs Head Camera)
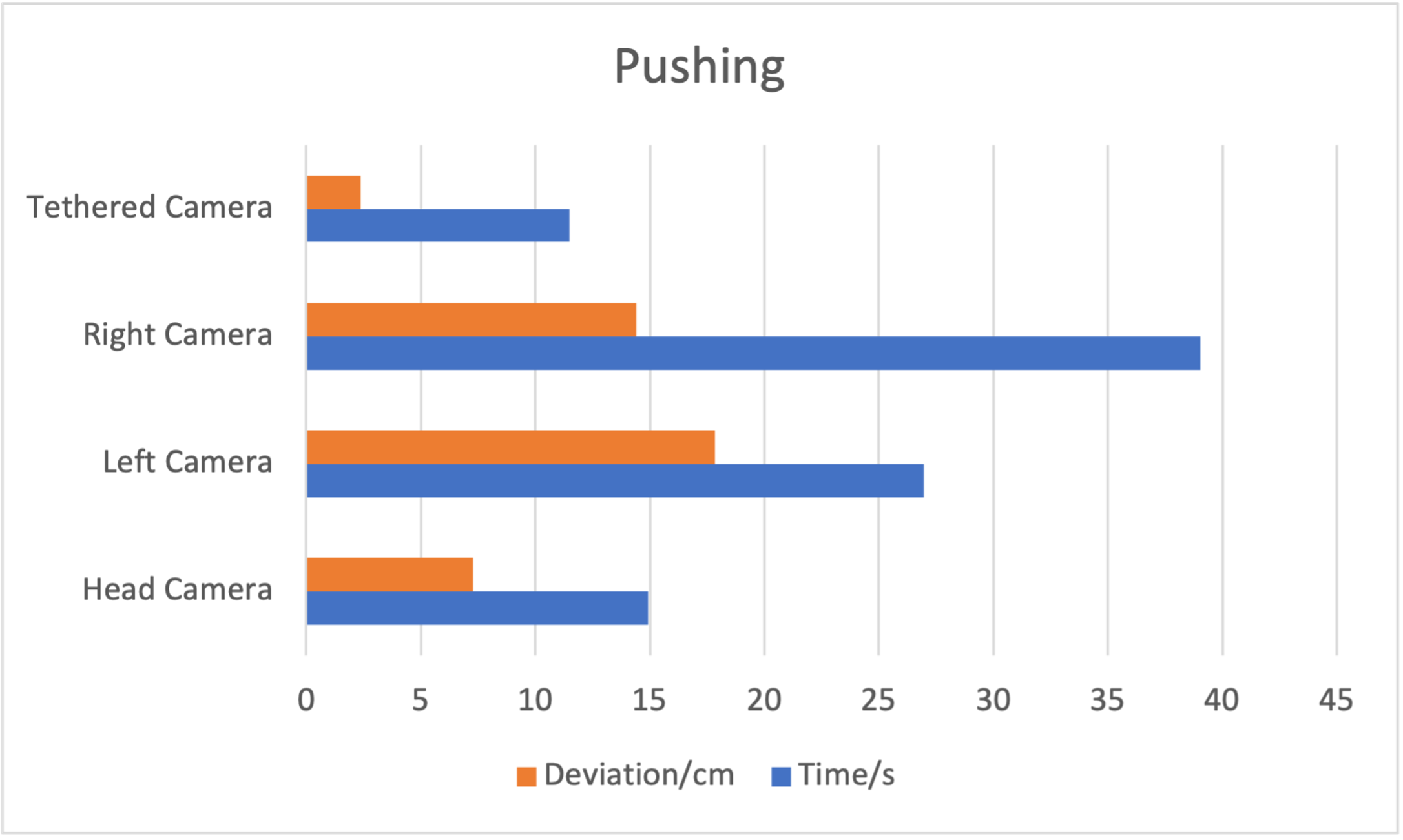
A Simple Analysis For User Performance in Pushing Task
